 SHARE
SHARE
Key Takeaways
- Converging edge computing and cloud strategies enables real-time data processing and analysis at the network edge.
- Challenges in convergence include data security and privacy concerns, network latency, and integration issues.
- Use cases for converged edge computing and cloud strategies span smart cities, industrial automation, and healthcare applications.
- Future trends in this space involve the integration of edge AI, 5G connectivity, and decentralized cloud architectures.
- The convergence of edge computing and cloud strategies has the potential to drive innovation and efficiency across various industries.
- Strategies in data and computation, particularly around omni-cloud and data access technologies .
The convergence of edge computing and cloud strategies represents a significant shift in the way organizations approach data processing and storage. This article explores the intersection of edge computing and cloud strategies, highlighting the benefits, challenges, use cases, and future trends in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Defining Edge Computing
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data near the source of data generation, closer to the edge of the network. This enables real-time data processing and analysis, reducing the need to send data to a centralized location. It also enhances low-latency and high-bandwidth applications, such as IoT devices and autonomous vehicles. This distributed computing paradigm improves overall system efficiency and responsiveness.
Exploring Cloud Strategies
Cloud strategies encompass a range of approaches for leveraging cloud computing resources to meet business needs. These strategies involve the deployment, management, and optimization of cloud services and infrastructure. They often focus on achieving scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility in delivering IT solutions.
PUBLIC CLOUD: Offers scalable and cost-effective resources on a pay-as-you-go model.
PRIVATE CLOUD: Provides dedicated and secure infrastructure for specific organizations.
HYBRID CLOUD: Combines public and private cloud environments for enhanced flexibility and control.
TIP: When exploring cloud strategies, consider the unique requirements of your organization and the potential benefits of each approach. It’s essential to align cloud strategies with business objectives and IT capabilities to maximize value and efficiency.
Challenges in Converging Edge Computing and Cloud Strategies
Let’s now examine some of the major challenges in implementing cloud strategies with edge
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Data security and privacy concerns are critical aspects of edge computing and cloud strategies. These concerns revolve around the protection of sensitive data, user privacy, and compliance with regulations. Ensuring secure data transmission and storage is essential for maintaining trust and integrity in converged systems.
- Data encryption and anonymization are key techniques for safeguarding sensitive information.
- Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify and mitigate potential risks.
- Implementing access controls and authentication mechanisms strengthens data security measures.
It is imperative to prioritize data security and privacy at every stage of convergence, from design to deployment, to build resilient and trustworthy systems.
Network Latency and Bandwidth Limitations
Network latency and bandwidth limitations are critical factors in the convergence of edge computing and cloud strategies. Reducing latency and optimizing bandwidth usage are essential for seamless integration and performance.
- LATENCY REDUCTION: Implement caching mechanisms and edge data processing to minimize round-trip times.
- BANDWIDTH OPTIMIZATION: Utilize data compression techniques and prioritize critical data transmission.
Proactively addressing these challenges can enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of converged edge computing and cloud strategies. It is imperative to consider these factors when designing and implementing converged solutions.
Benefits of Convergence
The convergence of Edge Computing and Cloud Strategies offers numerous benefits for organizations. It enables real-time data processing at the edge, reducing latency and enhancing responsiveness. Additionally, it optimizes bandwidth usage by processing data closer to the source, leading to more efficient network utilization. This convergence also facilitates seamless integration of edge devices with cloud services, creating a unified and scalable infrastructure.
- Improved real-time data processing
- Optimized bandwidth usage
- Seamless integration with cloud services
TIP: Organizations can leverage the benefits of convergence to enhance operational efficiency and drive innovation in their digital transformation initiatives.
Integration and Interoperability Issues
Edge computing and cloud convergence presents challenges in terms of integration and interoperability. This convergence requires seamless connectivity and compatibility between edge devices and cloud infrastructure. Interoperability standards and protocols play a crucial role in ensuring smooth communication and data exchange between the edge and the cloud.
To address these challenges, organizations must prioritize the development and adoption of open standards and protocols. This approach facilitates the integration of diverse edge devices and cloud platforms, enabling cohesive and efficient operations. Additionally, establishing clear API specifications and interfaces is essential for enabling seamless communication and data transfer across the edge-cloud ecosystem.
An important consideration is the management of data formats and structures across the edge and cloud environments. Consistent data formatting and structuring are vital for enabling interoperability and ensuring that data can be effectively processed and utilized across the entire edge-cloud architecture.
It is crucial to establish robust security measures and authentication protocols to safeguard data integrity and privacy. This includes implementing secure communication channels, encryption mechanisms, and access control policies to mitigate the risks associated with data exchange and integration across the edge and cloud.
Use Cases and Applications of Converged Edge
Computing and Cloud Strategies
Smart Cities and IoT
Smart cities leverage IoT devices and sensors to optimize urban infrastructure, enhance public services, and improve overall quality of life. These interconnected systems enable real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making, leading to more efficient resource allocation and sustainable development.
- Smart traffic management: Utilizing IoT sensors and edge computing to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance road safety.
- Environmental monitoring: Deploying IoT devices to monitor air quality, noise levels, and environmental conditions for better urban planning and pollution control.
TIP: The convergence of edge computing and cloud strategies in smart cities requires robust security measures and seamless integration to ensure reliable and secure operations.
Healthcare and Telemedicine
In the realm of healthcare and telemedicine, the convergence of edge computing and cloud strategies is revolutionizing patient care and medical services. This convergence enables real-time monitoring of patient vitals, remote diagnostics, and seamless access to medical records. Additionally, it facilitates the deployment of AI-driven predictive analytics for early disease detection and personalized treatment plans.
- Improved patient outcomes through remote monitoring and timely interventions
- Enhanced efficiency in telemedicine consultations and diagnosis
- Secure and scalable infrastructure for storing and accessing medical data
PRO TIP: Ensure compliance with healthcare regulations and data privacy laws when implementing converged solutions for healthcare and telemedicine.
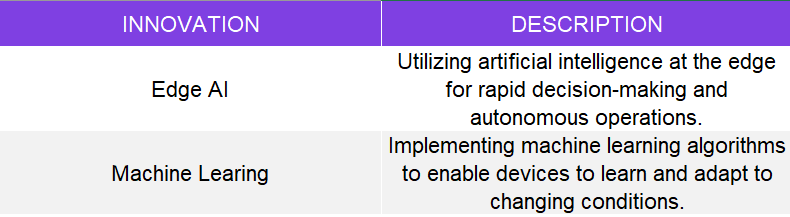
Edge AI and Machine Learning
Edge AI and Machine Learning are revolutionizing the way data is processed and analyzed at the edge of the network. This convergence enables real-time decision-making and advanced analytics, empowering devices to process and act on data locally.
KEY INNOVATIONS:
Decentralized and Distributed Cloud Architectures play a crucial role in supporting the scalability and resilience of edge computing. By distributing cloud resources closer to the edge, organizations can achieve low-latency, high-throughput, and fault-tolerant architectures.
TIP: Embracing decentralized and distributed cloud architectures can enhance the performance and reliability of edge computing solutions
5G and Edge-to-Cloud Connectivity
The 5G network’s high-speed, low-latency capabilities enable seamless connectivity between edge devices and the cloud. This connectivity empowers real-time data processing and analysis, enhancing edge computing applications. Furthermore, it facilitates rapid data transmission and supports mission-critical operations in various industries.
- Improved latency and bandwidth for time-sensitive applications
- Enhanced reliability and resilience for critical operations
- Expanded network capacity to accommodate growing data demands
TIP: Leverage 5G and edge-to-cloud connectivity to unlock new possibilities for real-time applications and critical use cases.
Decentralized and Distributed Cloud Architectures
Edge computing and cloud strategies are rapidly evolving, paving the way for decentralized and distributed cloud architectures.
This architectural shift emphasizes proximity to data sources and distributed processing, enabling low-latency and high-throughput applications.
- Edge computing and cloud convergence drives the need for dynamic resource allocation and elastic scaling to meet fluctuating demand.
- Decentralized and distributed cloud architectures facilitate resilient and fault-tolerant systems, enhancing reliability and availability.
TIP: Embrace decentralized and distributed cloud architectures to optimize performance, resilience, and scalability for edge computing and cloud strategies.
The future of edge computing and cloud strategies lies in the seamless integration of edge AI and machine learning, leveraging 5G for pervasive connectivity, and embracing the potential of decentralized and distributed cloud architectures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the convergence of Edge Computing and Cloud Strategies presents a transformative shift in the way organizations approach data processing and computing. By understanding the benefits and challenges associated with this convergence, businesses can effectively leverage the combined power of Edge Computing and Cloud Strategies to drive innovation and efficiency. As use cases in smart cities, industrial automation, and healthcare continue to demonstrate the potential of this convergence, it is evident that the future of Edge Computing and Cloud Strategies lies in innovative applications, AI, machine learning, and decentralized architectures. This evolution signifies a paradigm shift towards a more interconnected and intelligent digital ecosystem.



